行业解决方案查看所有行业解决方案
IDA 用于解决软件行业的关键问题。
发布时间:2022-10-11 17: 28: 46
Below is the full source code of a sample plugin. It performs a quite useful transformation of the pseudocode: replaces zeroes in pointer contexts with NULLs. A NULL immediately conveys the idea that the current expression is pointer-related. This is especially useful for unknown function arguments.
The plugin is fully automatic. It hooks to the decompiler events and waits for the pseudocode to be ready. At that moment it takes control and modifies the ctree.
The conversion is performed by the convert_zeroes() function. It visits all expressions of the ctree and checks for pointer contexts. If a expression has a pointer type, then the make_null_if_zero() function is called for it. This function checks if the expression is a zero constant and converts it if necessary.
The plugin can be turned on or off by its menu item in the Plugins submenu.
The code is short and straightforward. Use it as a template for your plugins.
/*
* Hex-Rays Decompiler project
* Copyright (c) 2007-2019 by Hex-Rays, support@hex-rays.com
* ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
*
* Sample plugin for Hex-Rays Decompiler.
* It automatically replaces zeroes in pointer contexts with NULLs.
* For example, expression like
*
* funcptr = 0;
*
* will be displayed as
*
* funcptr = NULL;
*
* Due to highly dynamic nature of the decompier output, we must
* use the decompiler events to accomplish the task. The plugin will
* wait for the ctree structure to be ready in the memory and will
* replace zeroes in pointer contexts with NULLs.
*
*/
#include
// Hex-Rays API pointer
hexdsp_t *hexdsp = NULL;
static bool inited = false;
static const char nodename[] = “$ hexrays NULLs”;
static const char null_type[] = “MACRO_NULL”;
//————————————————————————–
// Is the plugin enabled?
// The user can disable it. The plugin will save the on/off switch in the
// current database.
static bool is_enabled(void)
{
netnode n(nodename); // use a netnode to save the state
return n.altval(0) == 0; // if the long value is positive, then disabled
}
//————————————————————————–
// If the expression is zero, convert it to NULL
static void make_null_if_zero(cexpr_t *e)
{
if ( e->is_zero_const() && !e->type.is_ptr() )
{ // this is plain zero, convert it
number_format_t &nf = e->n->nf;
nf.flags = enum_flag();
nf.serial = 0;
nf.type_name = null_type;
e->type = tinfo_t::get_stock(STI_PVOID);
}
}
//————————————————————————–
// Convert zeroes of the ctree to NULLs
static void convert_zeroes(cfunc_t *cfunc)
{
// To represent NULLs, we will use the MACRO_NULL enumeration
// Normally it is present in the loaded tils but let’s verify it
if ( !get_named_type(NULL, null_type, NTF_TYPE) )
{
msg(“%s type is missing, cannot convert zeroes to NULLs\n”, null_type);
return;
}
// We derive a helper class from ctree_visitor_t
// The ctree_visitor_t is a base class to derive
// ctree walker classes.
// You have to redefine some virtual functions
// to do the real job. Here we redefine visit_expr() since we want
// to examine and modify expressions.
struct ida_local zero_converter_t : public ctree_visitor_t
{
zero_converter_t(void) : ctree_visitor_t(CV_FAST) {}
int idaapi visit_expr(cexpr_t *e)
{
// verify if the current expression has pointer expressions
// we handle the following patterns:
// A. ptr = 0;
// B. func(0); where argument is a pointer
// C. ptr op 0 where op is a comparison
switch ( e->op )
{
case cot_asg: // A
if ( e->x->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->y);
break;
case cot_call: // B
{
carglist_t &args = *e->a;
for ( int i=0; i < args.size(); i++ ) // check all arguments
{
carg_t &a = args[i];
if ( a.formal_type.is_ptr_or_array() )
make_null_if_zero(&a);
}
}
break;
case cot_eq: // C
case cot_ne:
case cot_sge:
case cot_uge:
case cot_sle:
case cot_ule:
case cot_sgt:
case cot_ugt:
case cot_slt:
case cot_ult:
// check both sides for zeroes
if ( e->y->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->x);
if ( e->x->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->y);
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0; // continue walking the tree
}
};
zero_converter_t zc;
// walk the whole function body
zc.apply_to(&cfunc->body, NULL);
}
//————————————————————————–
// This callback will detect when the ctree is ready to be displayed
// and call convert_zeroes() to create NULLs
static ssize_t idaapi callback(void *, hexrays_event_t event, va_list va)
{
if ( event == hxe_maturity )
{
cfunc_t *cfunc = va_arg(va, cfunc_t*);
ctree_maturity_t mat = va_argi(va, ctree_maturity_t);
if ( mat == CMAT_FINAL ) // ctree is ready, time to convert zeroes to NULLs
convert_zeroes(cfunc);
}
return 0;
}
//————————————————————————–
// Initialize the plugin.
int idaapi init(void)
{
if ( !init_hexrays_plugin() )
return PLUGIN_SKIP; // no decompiler
if ( is_enabled() ) // null plugin is enabled?
{
install_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
const char *hxver = get_hexrays_version();
msg(“Hex-rays version %s has been detected, %s ready to use\n”, hxver, PLUGIN.wanted_name);
}
inited = true;
return PLUGIN_KEEP;
}
//————————————————————————–
void idaapi term(void)
{
if ( inited )
{
// clean up
remove_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
term_hexrays_plugin();
}
}
//————————————————————————–
bool idaapi run(size_t)
{
// since all real work is done in the callbacks, use the main plugin entry
// to turn it on and off.
// display a message explaining the purpose of the plugin:
int code = askbuttons(
“~E~nable”,
“~D~isable”,
“~C~lose”,
–1,
“AUTOHIDE NONE\n”
“Sample plugin for Hex-Rays decompiler.\n”
“\n”
“This plugin is fully automatic.\n”
“It detects zeroes in pointer contexts and converts them into NULLs.\n”
“\n”
“The current state of the plugin is: %s\n”,
is_enabled() ? “ENABLED” : “DISABLED”);
switch ( code )
{
case –1: // close
break;
case 0: // disable
case 1: // enable
netnode n;
n.create(nodename);
n.altset(0, code == 0);
if ( code )
install_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
else
remove_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
info(“The %s plugin has been %s.”, PLUGIN.wanted_name, code ? “ENABLED” : “DISABLED”);
break;
}
return true;
}
//————————————————————————–
static char comment[] = “Sample2 plugin for Hex-Rays decompiler”;
//————————————————————————–
//
// PLUGIN DESCRIPTION BLOCK
//
//————————————————————————–
plugin_t PLUGIN =
{
IDP_INTERFACE_VERSION,
0, // plugin flags
init, // initialize
term, // terminate. this pointer may be NULL.
run, // invoke plugin
comment, // long comment about the plugin
// it could appear in the status line
// or as a hint
“”, // multiline help about the plugin
“Hex-Rays NULL converter”, // the preferred short name of the plugin
“” // the preferred hotkey to run the plugin
};
中文翻译如下:
以下是一个示例插件的完整源代码。它执行一个非常有用的伪代码转换:将指针上下文中的零替换为NULL。NULL立即传达了当前表达式与指针相关的概念。这对于未知的函数参数尤其有用。
该插件是完全自动化的。它钩入反编译器事件并等待伪代码准备就绪。在那一刻,它接管并修改ctree。
转换是由convert_zeroes()函数执行的。它访问ctree的所有表达式并检查指针上下文。如果一个表达式具有指针类型,则为它调用make_null_if_zero()函数。此函数检查表达式是否为零常量并在必要时进行转换。
该插件可以通过插件子菜单中的菜单项打开或关闭。
代码短小简单。可以将其用作插件的模板。
/*
* Hex-Rays Decompiler project
* Copyright (c) 2007-2019 by Hex-Rays, support@hex-rays.com
* ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
*
* Sample plugin for Hex-Rays Decompiler.
* It automatically replaces zeroes in pointer contexts with NULLs.
* For example, expression like
*
* funcptr = 0;
*
* will be displayed as
*
* funcptr = NULL;
*
* Due to highly dynamic nature of the decompier output, we must
* use the decompiler events to accomplish the task. The plugin will
* wait for the ctree structure to be ready in the memory and will
* replace zeroes in pointer contexts with NULLs.
*
*/
#include
// Hex-Rays API pointer
hexdsp_t *hexdsp = NULL;
static bool inited = false;
static const char nodename[] = “$ hexrays NULLs”;
static const char null_type[] = “MACRO_NULL”;
//————————————————————————–
// Is the plugin enabled?
// The user can disable it. The plugin will save the on/off switch in the
// current database.
static bool is_enabled(void)
{
netnode n(nodename); // use a netnode to save the state
return n.altval(0) == 0; // if the long value is positive, then disabled
}
//————————————————————————–
// If the expression is zero, convert it to NULL
static void make_null_if_zero(cexpr_t *e)
{
if ( e->is_zero_const() && !e->type.is_ptr() )
{ // this is plain zero, convert it
number_format_t &nf = e->n->nf;
nf.flags = enum_flag();
nf.serial = 0;
nf.type_name = null_type;
e->type = tinfo_t::get_stock(STI_PVOID);
}
}
//————————————————————————–
// Convert zeroes of the ctree to NULLs
static void convert_zeroes(cfunc_t *cfunc)
{
// To represent NULLs, we will use the MACRO_NULL enumeration
// Normally it is present in the loaded tils but let’s verify it
if ( !get_named_type(NULL, null_type, NTF_TYPE) )
{
msg(“%s type is missing, cannot convert zeroes to NULLs\n”, null_type);
return;
}
// We derive a helper class from ctree_visitor_t
// The ctree_visitor_t is a base class to derive
// ctree walker classes.
// You have to redefine some virtual functions
// to do the real job. Here we redefine visit_expr() since we want
// to examine and modify expressions.
struct ida_local zero_converter_t : public ctree_visitor_t
{
zero_converter_t(void) : ctree_visitor_t(CV_FAST) {}
int idaapi visit_expr(cexpr_t *e)
{
// verify if the current expression has pointer expressions
// we handle the following patterns:
// A. ptr = 0;
// B. func(0); where argument is a pointer
// C. ptr op 0 where op is a comparison
switch ( e->op )
{
case cot_asg: // A
if ( e->x->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->y);
break;
case cot_call: // B
{
carglist_t &args = *e->a;
for ( int i=0; i < args.size(); i++ ) // check all arguments
{
carg_t &a = args[i];
if ( a.formal_type.is_ptr_or_array() )
make_null_if_zero(&a);
}
}
break;
case cot_eq: // C
case cot_ne:
case cot_sge:
case cot_uge:
case cot_sle:
case cot_ule:
case cot_sgt:
case cot_ugt:
case cot_slt:
case cot_ult:
// check both sides for zeroes
if ( e->y->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->x);
if ( e->x->type.is_ptr() )
make_null_if_zero(e->y);
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0; // continue walking the tree
}
};
zero_converter_t zc;
// walk the whole function body
zc.apply_to(&cfunc->body, NULL);
}
//————————————————————————–
// This callback will detect when the ctree is ready to be displayed
// and call convert_zeroes() to create NULLs
static ssize_t idaapi callback(void *, hexrays_event_t event, va_list va)
{
if ( event == hxe_maturity )
{
cfunc_t *cfunc = va_arg(va, cfunc_t*);
ctree_maturity_t mat = va_argi(va, ctree_maturity_t);
if ( mat == CMAT_FINAL ) // ctree is ready, time to convert zeroes to NULLs
convert_zeroes(cfunc);
}
return 0;
}
//————————————————————————–
// Initialize the plugin.
int idaapi init(void)
{
if ( !init_hexrays_plugin() )
return PLUGIN_SKIP; // no decompiler
if ( is_enabled() ) // null plugin is enabled?
{
install_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
const char *hxver = get_hexrays_version();
msg(“Hex-rays version %s has been detected, %s ready to use\n”, hxver, PLUGIN.wanted_name);
}
inited = true;
return PLUGIN_KEEP;
}
//————————————————————————–
void idaapi term(void)
{
if ( inited )
{
// clean up
remove_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
term_hexrays_plugin();
}
}
//————————————————————————–
bool idaapi run(size_t)
{
// since all real work is done in the callbacks, use the main plugin entry
// to turn it on and off.
// display a message explaining the purpose of the plugin:
int code = askbuttons(
“~E~nable”,
“~D~isable”,
“~C~lose”,
–1,
“AUTOHIDE NONE\n”
“Sample plugin for Hex-Rays decompiler.\n”
“\n”
“This plugin is fully automatic.\n”
“It detects zeroes in pointer contexts and converts them into NULLs.\n”
“\n”
“The current state of the plugin is: %s\n”,
is_enabled() ? “ENABLED” : “DISABLED”);
switch ( code )
{
case –1: // close
break;
case 0: // disable
case 1: // enable
netnode n;
n.create(nodename);
n.altset(0, code == 0);
if ( code )
install_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
else
remove_hexrays_callback(callback, NULL);
info(“The %s plugin has been %s.”, PLUGIN.wanted_name, code ? “ENABLED” : “DISABLED”);
break;
}
return true;
}
//————————————————————————–
static char comment[] = “Sample2 plugin for Hex-Rays decompiler”;
//————————————————————————–
//
// PLUGIN DESCRIPTION BLOCK
//
//————————————————————————–
plugin_t PLUGIN =
{
IDP_INTERFACE_VERSION,
0, // plugin flags
init, // initialize
term, // terminate. this pointer may be NULL.
run, // invoke plugin
comment, // long comment about the plugin
// it could appear in the status line
// or as a hint
“”, // multiline help about the plugin
“Hex-Rays NULL converter”, // the preferred short name of the plugin
“” // the preferred hotkey to run the plugin
};
展开阅读全文
︾
读者也喜欢这些内容:
IDA pro修改so教程 IDA pro修改exe
在逆向分析与二进制安全研究中,IDA pro作为主流静态分析工具,其强大的反汇编与重构能力,广泛应用于ELF格式的so库与PE格式的exe文件修改。通过IDA pro修改so文件,可用于Android应用补丁、破解函数逻辑、绕过验证;而对exe文件的修改则常用于Windows下的补丁、功能改写与程序定制。掌握IDA pro修改so与exe的流程,不仅能提升分析效率,更是逆向工程技能的基础能力。以下内容将系统讲解IDA pro修改so教程,IDA pro修改exe两大操作场景的具体步骤,帮助用户完整掌握二进制修改流程。...
阅读全文 >
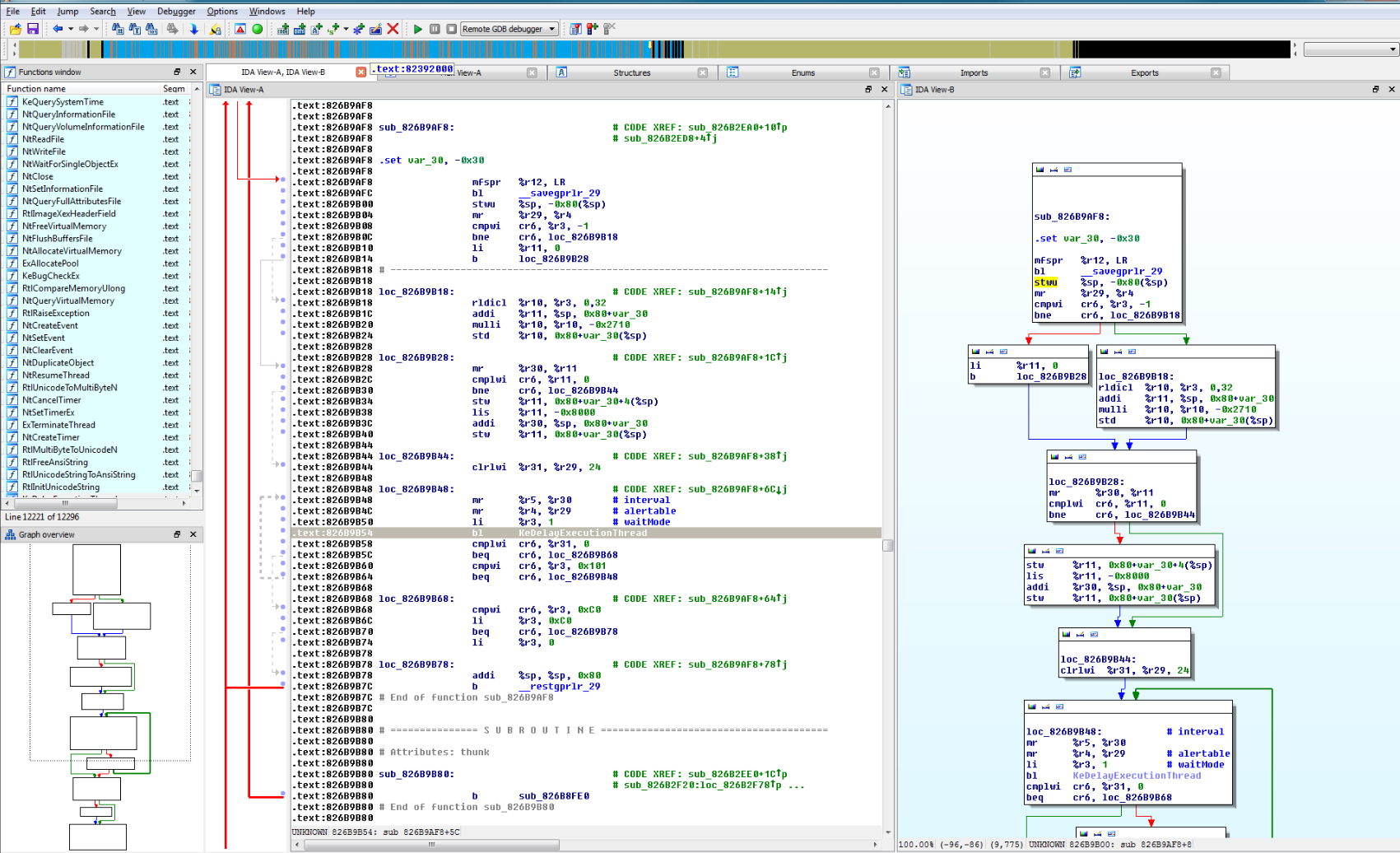
IDA Pro的扩展功能如何使用 IDA Pro脚本有哪些高级用法
作为全球最受欢迎的反汇编与逆向分析工具之一,IDA Pro(Interactive Disassembler Professional) 不仅提供强大的静态分析能力,更具备灵活的扩展机制与脚本系统。借助这些功能,逆向工程师可以深入分析大型程序,自动化重复流程,乃至构建定制化的逆向框架。本文将围绕“IDA Pro的扩展功能如何使用”以及“IDA Pro脚本有哪些高级用法”两个主题进行全面剖析,帮助你掌握其进阶操作技巧,显著提升逆向分析效率与深度。...
阅读全文 >
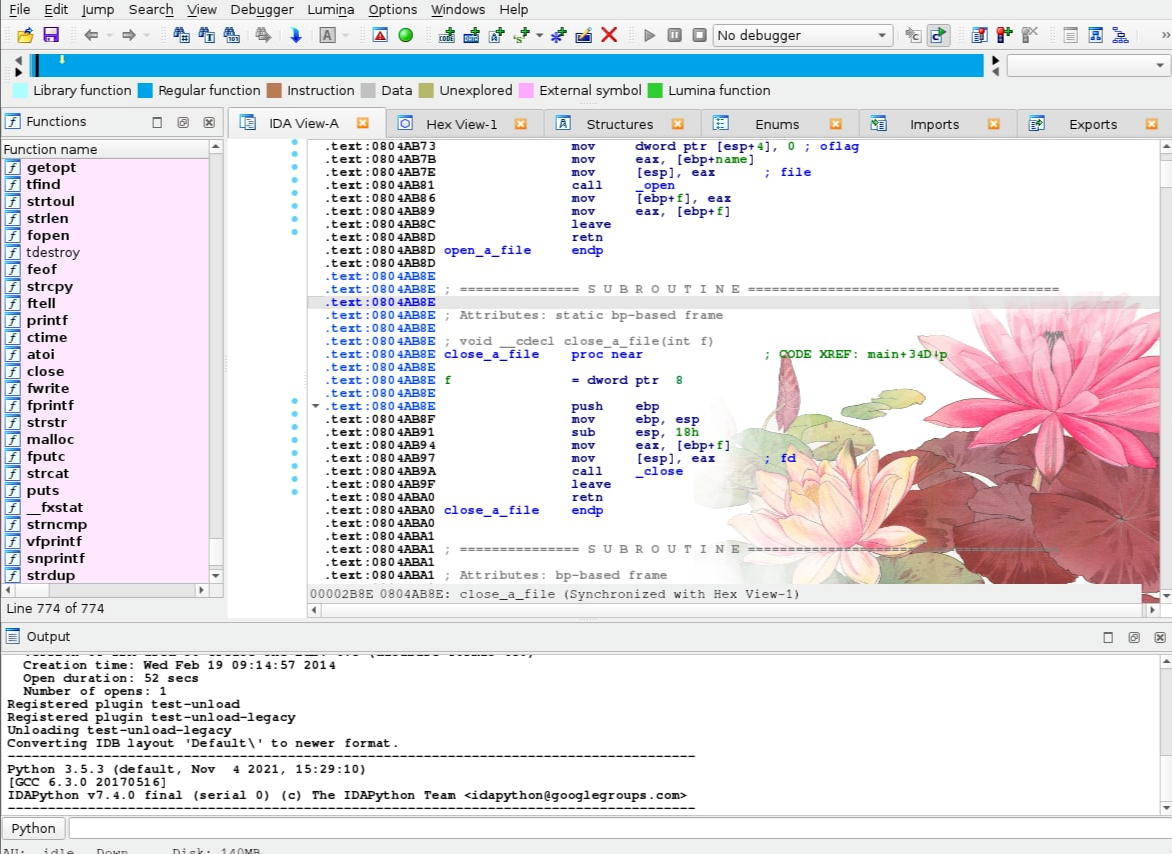
IDA Pro如何批量分析文件 IDA Pro自动化脚本怎么写
说起逆向工程分析工具,不少人第一个想到的就是IDA Pro。只要掌握了IDA Pro自动化的一些小技巧,比如批量处理文件、用脚本自动分析,逆向工作的效率就会蹭蹭往上涨。这篇文章我就给大家聊聊IDA Pro如何批量分析文件 IDA Pro自动化脚本怎么写。...
阅读全文 >
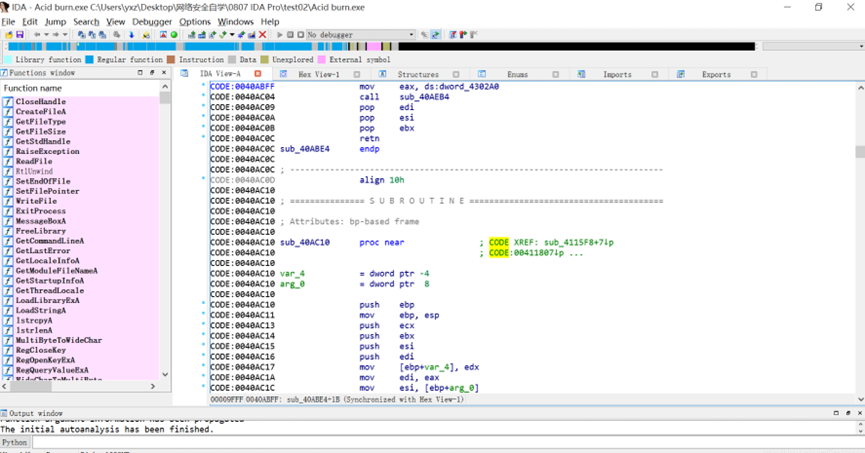
怎么用IDA软件反汇编功能学习汇编指令 IDA反汇编功能如何进行多平台二进制分析
说到反汇编分析,很多人第一时间就会想到IDA。这款工具可以说是做逆向工程的“神器”,不管是学习汇编指令还是分析二进制文件,都非常给力。如果你是个初学者,刚接触反汇编,可能会对IDA的一些功能感到陌生,比如怎么用IDA软件反汇编功能学习汇编指令 IDA反汇编功能如何进行多平台二进制分析。别急,今天就带你一步步搞清楚。...
阅读全文 >